Coprinopsis atramentaria extract, its organic acids, and synthesized glucuronated and methylated derivatives as antibacterial and antifungal agents
Abstract
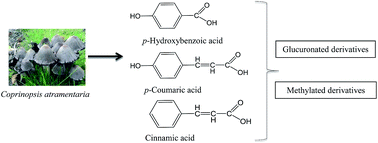
Despite the available data regarding antimicrobial activity of phenolic acids, studies dealing with the effects of their metabolites or derivatives are scarce. Therefore, the antimicrobial and demelanizing activities of Coprinopsis atramentaria extract, its organic acids, and methylated and glucuronated derivatives were evaluated. The antifungal activity was stronger than the antibacterial effects. In general, individual compounds (mostly organic acids) exhibited higher activity than the extract and even higher than the standards used in the assays. Methylated derivatives presented the highest demelanizing activity toward Aspergillus niger, A. fumigatus and Penicillium verrucosum var. cyclopium. The inclusion of methyl groups in the parental compound (CoAM1, CoAM2 and CoAM3) strongly increased antibacterial and antifungal activities of CoA, while the inclusion of acetyl groups (CoAGP) increased the antifungal activity but the antibacterial properties were maintained. For HA and CA, the inclusion of methyl groups (HAM1, HAM2, HAM3 and CAM) increased the demelanizing activity, but decreased the antimicrobial properties. The present work contributes to the knowledge of the mechanisms involved in the antimicrobial properties of organic acids namely, phenolic acids, usually present in mushrooms. Organic acids, and methylated and glucuronated derivatives could be used as antimicrobial agents.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...