Inhibition of allergic airway inflammation through the blockage of NF-κB activation by ellagic acid in an ovalbumin-induced mouse asthma model
Abstract
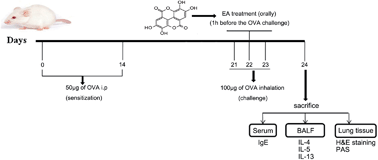
Allergic asthma is a complex inflammatory disease characterized by airway hyperresponsiveness, eosinophilic inflammation and the hypersecretion of mucus by goblet cells. Ellagic acid (EA), a natural polyphenolic compound present as ellagitannins in fruits and fruit juices, has been reported to show potent anti-inflammatory properties in various diseases. We aimed to investigate the effects of EA in an ovalbumin (OVA)-induced mouse asthma model and to explore its potential mechanism of action. Our results showed that EA resulted in a significant reduction in lung eosinophilia, increased Th2 cytokines in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and increased OVA-induced specific IgE in serum samples. Moreover, histological examination showed that EA markedly inhibited lung eosinophilic inflammation and goblet cell hyperplasia. In addition, EA attenuated the development of airway hyperresponsiveness and blocked NF-κB activation. These results demonstrate that EA shows obvious anti-inflammatory effects in OVA-induced asthma in a mouse model, possibly through inhibiting NF-κB activation. Therefore it may be a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of allergic asthma.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...