Protective effects of garcinol on dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis in rats
Abstract
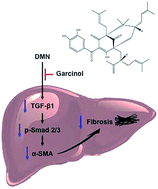
Garcinol, a polyisoprenylated benzophenone derivative, mainly isolated from Garcinia indica fruit rind, has been suggested to exhibit many biological benefits including antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumor activities. The aim of this study is to evaluate the protective effects of garcinol on dimethylnitrosamine (DMN)-induced liver fibrosis in rats. The administration of DMN for six consecutive weeks resulted in the decrease of body weights, the elevation of serum aminotransferases, as well as histological lesions in livers. However, oral administration of garcinol remarkably inhibited the elevation of aspartate transaminase (AST) and relieved liver damage induced by DMN. Furthermore, our results revealed that garcinol not only effectively reduced the accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) components but also inhibited the expression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) in livers. The expression of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) and the phosphorylation of Smad 2 and Smad 3 were also suppressed by garcinol supplementation. In conclusion, our current study suggested that garcinol exerted hepatoprotective and anti-fibrotic effects against DMN-induced liver injury in rats.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...