The impact of biochar on the bioaccessibility of 14C-phenanthrene in aged soil
Abstract
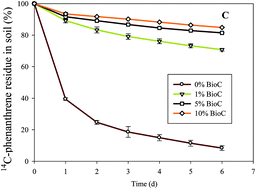
Biochar is a carbon rich product from the incomplete combustion of biomass and it has been shown to reduce bioavailability of organic contaminants through adsorption. This study investigated the influence of 0%, 1%, 5% and 10% of two different particle sized wood biochars (≤2 mm and 3–7 mm) on the bioaccessibility of 14C-phenanthrene (10 mg kg−1) in aged soil. The extent of 14C-phenanthrene mineralisation by phenanthrene-degrading Pseudomonas sp. inoculum was monitored over a 14 day period in respirometric assays and compared to hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPCD) aqueous extraction. Notably, biochar amendments showed significant reduction in extents of mineralisation and HPCD extraction. Linear correlations between HPCD extractability and the total amount mineralised revealed good correlations, with 2 mm biochar showing a best fit (r2 = 0.97, slope = 1.11, intercept = 1.72). Biochar reduced HPCD extractability and bioaccessibility of 14C-phenanthrene to microorganisms in a similar manner. Biochar can aid risk reduction to phenanthrene exposure to biota in soil and HPCD can serve as a useful tool to assess the extent of exposure in biochar-amended soils.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...