Using multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs) for oilfield produced water treatment with environmentally acceptable endpoints†
Abstract
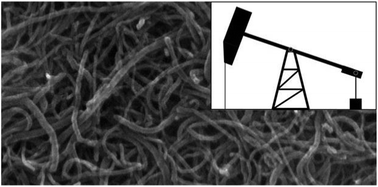
In this study, multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs) were employed to remove benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylenes (BTEX) from low and high salinity water pre-equilibrated with crude oil. The treatment endpoint of crude oil-contaminated water is often controlled by BTEX compounds owing to their higher aqueous solubility and human-health toxicity compared to other hydrocarbons. The MWNT sorbent was extensively characterized and the depletion of the organic sorbate from the produced water was monitored by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and total organic carbon (TOC) analyses. The equilibrium sorptive removal of BTEX followed the order: ethylbenzene/o-xylene > m-xylene > toluene > benzene in the presence of other competing organics in produced water. Sorption mechanisms were explored through the application of a variety of kinetics and equilibrium models. Pseudo 2nd order kinetics and Freundlich equilibrium models were the best at describing BTEX removal from produced water. Hydrophobic interactions between the MWNTs and BTEX, as well as the physical characteristics of the sorbate molecules, were regarded as primary factors responsible for regulating competitive adsorption. Salinity played a critical role in limiting sorptive removal, with BTEX and total organic carbon (TOC) removal falling by 27% and 25%, respectively, upon the introduction of saline conditions. Results suggest that MWNTs are effective in removing risk-driving BTEX compounds from low-salinity oilfield produced water.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...