Solid-state carbon-13 NMR and computational characterization of the N719 ruthenium sensitizer adsorbed on TiO2 nanoparticles†
Abstract
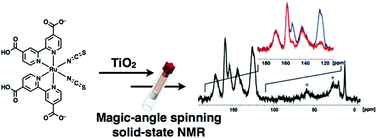
The ruthenium-containing sensitizing dye N719 grafted on TiO2 nanoparticles was investigated by solid-state NMR. The carbon resonances are assigned by means of 13C cross-polarized dipolar dephasing experiments. DFT calculations of the carbon magnetic shielding tensors accurately describe the changes in chemical shifts observed upon grafting onto a titania surface via one or two carboxylic functions in the plane defined by the two isothiocyanate groups.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...