In situ synthesis of uniform Fe2O3/BiOCl p/n heterojunctions and improved photodegradation properties for mixture dyes†
Abstract
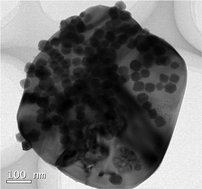
The xFe2O3/yBiOCl composites (xFe/yBi, x/y = 0/100, 5/100, 10/100, 20/100, 30/100 and 40/100 molar ratios) are prepared for the first time through an in situ hydrolysis method under hydrothermal conditions. The samples are characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), selected area electron diffraction (SAED) and UV-visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV-DRS). The photodegradation performances of the xFe/yBi samples are investigated using a simulated industrial wastewater mixture containing both rhodamine B (RhB) and methyl orange (MO). The uniform Fe2O3 nanocubes are found to be well distributed on the BiOCl nanosheets. Moreover, the xFe/yBi photocatalysts exhibit unexpectedly higher efficiencies than bare BiOCl or Fe2O3 under ultraviolet light irradiation (λ ≤ 420 nm). Specifically, the degradation rates of the xFe/yBi samples at x/y = 5/100 and 10/100 are four times higher than that of bare BiOCl for MO–RhB mixed dye solutions. Their high photocatalytic activities are mainly attributed to the formation of stable p/n heterojunctions between Fe2O3 and BiOCl, which greatly improve the separation of photogenerated carriers. Importantly, the highly efficient and inexpensive xFe/yBi p/n heterojunctions are expected to be useful in practical industrial wastewater applications involving complicated toxic components.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...