Two isoreticular metal–organic frameworks with CdSO4-like topology: selective gas sorption and drug delivery†
Abstract
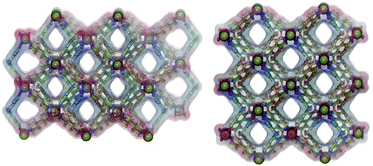
Two isoreticular metal–organic frameworks with chemical formulae [Cu(L)(4,4′-bipy)(H2O)]n 1.5nCH3CN (1) and [Cu(L)(4,4′-bipy)(H2O)]n·4nH2O (2) (H2L = diphenylmethane-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid) were synthesized and structurally characterized. They show the CdSO4 (65 8) net and have an obvious 1D channel that is spread along the crystallographic c axis. More importantly, 1 shows high selectivity for H2 over N2 and CO2 at low pressure, which could be confirmed via computational calculations using the Connolly algorithm to reveal the size and shape of accessible voids. The incorporation of the drug 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) into the desolvated 1 was around 27.5 wt% per gram of the dehydrated 1. 5-FU is released in a highly controlled and progressive fashion with 61% of the drug released after 95 hours. In addition, we have applied molecular docking calculations to investigate the preferred conformation of 5-FU molecules upon binding to MOF 1. These calculations provide a structural basis to explain the 5-FU release from MOF 1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...