The influence of NaYF4:Yb,Er size/phase on the multimodality of co-encapsulated magnetic photon-upconverting polymeric nanoparticles†
Abstract
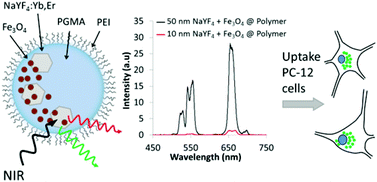
We report the synthesis, characterisation and evaluation of the in vitro biocompatibility of polymeric nanoparticles with both magnetic and upconverting fluorescent properties. The particles consist of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and upconverting NaYF4:Yb,Er nanoparticles co-encapsulated within a poly(glycidyl methacrylate) sphere. Two different upconverting nanoparticles (10 nm α-NaYF4:Yb,Er and 50 nm β-NaYF4:Yb,Er) were synthesised and the optical and magnetic properties of the composite polymeric nanoparticle systems assessed by near infra-red laser spectroscopy, SQUID magnetometry and proton relaxometry. A live-dead assay was used to assess the viability of PC-12 neural cells incubated with varying concentrations of the nanoparticles. The composite nanoparticles produced no observed impact on cellular viability even at concentrations as high as 1000 μg mL−1. Confocal microscopy revealed uptake of nanoparticles by PC-12 cells and peri-nuclear cytoplasmic localisation. Both particle systems show favourable magnetic properties. However, only the nanospheres containing 50 nm β-NaYF4:Yb,Er were suitable for optical tracking because the presence of iron oxide within the composites imparts a significant quenching of the upconversion emission. This study demonstrates the size and phase of the upconverting nanoparticles are important parameters that have to be taken into account in the design of multimodal nanoparticles using co-encapsulation strategies.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...