Mechanistic insights into hydride transfer for catalytic hydrogenation of CO2 with cobalt complexes†
Abstract
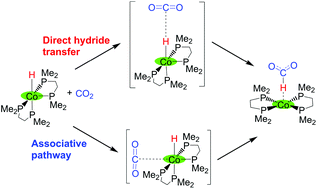
The catalytic hydrogenation of CO2 to formate by Co(dmpe)2H can proceed via direct hydride transfer or via CO2 coordination to Co followed by reductive elimination of formate. The different nature of the rate-determining step in the two mechanisms may provide new insights into designing catalysts with improved performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...