Bismuth induced enhanced green emission from terbium ions and their complex in thin films†
Abstract
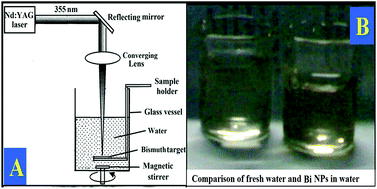
Bismuth nanoparticles (NPs) have been prepared by the pulsed laser ablation technique using the third harmonics of a Nd-YAG laser. UV-absorption and TEM micrographs show Bi NPs of spherical shape with the average particle size ranging from 15 to 20 nm. These NPs were dispersed with Tb3+ ions and their complex with salicylic acid (Sal) in polyvinyl alcohol to obtain thin films. The influence of Bi NPs on the emissive properties of Tb3+ ions and the [Tb(Sal)3(phen)] complex has been studied by luminescence spectroscopy using 266 nm and 355 nm as excitation wavelengths. The luminescence intensity of Tb3+ ions complexed with Sal in the thin polymer films increased significantly as compared to the Tb3+ ions in the presence of Bi NPs on excitation at 355 nm. However, terbium ions in the case of the [Tb(Sal)3(phen)] complex together with NPs show an intense and extended emission spectrum in the 375–700 nm range for transitions arising from 5D3 and 5D4 levels to different 7FJ levels on 266 nm excitation. The luminescence enhancement has also been supported by lifetime measurements.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...