Synthesis, characterization, DNA binding, cleavage activity and cytotoxicity of copper(ii) complexes†
Abstract
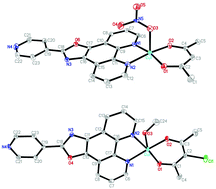
Three new mononuclear copper(II) complexes, [Cu(L2)]2+ (1), [Cu(acac)(L)]+ (2), and [Cu(acac-Cl)(L)]+ (3) (L = 2-(4-pyridine)oxazo[4,5-f]1,10-phenanthroline (4-PDOP); acac = acetylacetone; acac-Cl = 3-chloroacetylacetone), have been synthesized and characterized by elemental analysis, high resolution mass spectrometry (Q-TOF), and IR spectroscopy. Two of the complexes were structurally characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction techniques. Their interactions with DNA were studied by UV-vis absorption and emission spectra, viscosity, thermal melting, DNA unwinding assay and CD spectroscopy. The nucleolytic cleavage activity of the compounds was carried out on double stranded pBR322 circular plasmid DNA by using a gel electrophoresis experiment in the presence and absence of an oxidant (H2O2). Active oxygen intermediates such as hydroxyl radicals and hydrogen peroxide generated in the presence of L and complexes 1–3 may act as active species for the DNA scission. The cytotoxicity of the complexes against HepG2 cancer cells was also studied.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...