Borate-based ligands with two soft heterocycle/thione groups and their sodium and bismuth complexes†
Abstract
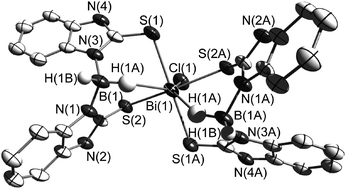
Two novel sodium complexes [NaBb] (1) (Bb = dihydrobis(2-mercapto-benzimidazolyl)borate) and [NaBtMe] (2) (BtMe = dihydrobis(2-mercapto-4-methylthiazolyl)borate) have been prepared and characterized by using two heterocycles, 2-mercapto-benzimidazole and 2-mercapto-4-methylthiazole, as well as NaBH4 as precursors. The dipodal boron centred soft ligands Bb and BtMe were prepared in situ. The reactivity of [NaBb] (1) and [NaBtMe] (2) towards Bi(III) ions has been studied. The resulting complex [BiBb2Cl] (3) contains an MS4 core with κ3-S,S,H coordination mode, while the complex [BiBtMe3] (4) with an MS6 core adopts a coordination mode κ2-S,S. A reaction of BiCl3 with the heterocyclic precursors 2-mercapto-benzimidazole (L1) and 2-mercapto-4-methylthiazole (L2) was also attempted; this afforded the monomeric [BiL14Cl2][BiL12Cl4] (5) and dimeric [BiL22(μ-Cl)Cl]2 (6) bismuth complexes. The bismuth complexes possess distorted octahedral geometries except 3 for which a face-capped octahedron is found. The presence of (B)H⋯Bi interactions has been identified by X-ray diffraction in 3 with a H⋯Bi distance of 2.58(1) Å which is uniquely short and unprecedented. Two of the synthesized complexes (4 and 5) have been investigated by luminescence spectroscopy. They feature emission bands in the solid state at room temperature at 674 (4) and 586 nm (5), which are hypsochromically shifted in (frozen) ethanolic solutions at 77 K to 618 and 537 nm, respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...