Noncovalent functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes as metal-free catalysts for the reduction of nitrobenzene†
Abstract
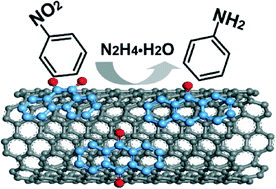
Multi-walled carbon nanotubes were functionalized with small organic molecules containing specific ketonic carbonyl groups through noncovalent van der Waals and π–π interactions. The comparison of intrinsic activities for a series of catalysts indicates that the carbonyl groups are active sites in the reduction of nitrobenzene, and the catalysts functionalized with phenanthraquinone exhibit relatively high activity and selectivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...