Förster resonance energy transfer and kinesin motor proteins
Abstract
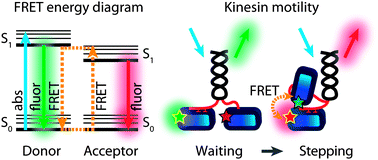
Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) is the phenomenon of non-radiative transfer of electronic excitations from a donor fluorophore to an acceptor, mediated by electronic dipole–dipole coupling. The transfer rate and, as a consequence, efficiency depend non-linearly on the distance between the donor and the acceptor. FRET efficiency can thus be used as an effective and accurate reporter of distance between two fluorophores and changes thereof. Over the last 50 years or so, FRET has been used as a spectroscopic ruler to measure conformations and conformational changes of biomolecules. More recently, FRET has been combined with microscopy, ultimately allowing measurement of FRET between a single donor and a single acceptor pair. In this review, we will explain the physical foundations of FRET and how FRET can be applied to biomolecules. We will highlight the power of the different FRET approaches by focusing on its application to the motor protein kinesin, which undergoes several conformational changes driven by enzymatic action, that ultimately result in unidirectional motion along microtubule filaments, driving active transport in the cell. Single-molecule and ensemble FRET studies of different aspects of kinesin have provided numerous insights into the complex chemomechanical mechanism of this fascinating protein.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Single-molecule optical spectroscopy

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...