High thermal sensitivity and the selectable upconversion color of Ln, Yb:Y6O5F8 nanotubes†
Abstract
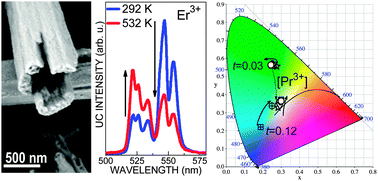
Yb3+-sensitized, Ln3+(Er3+, Pr3+)-doped Y6O5F8 micron-sized bundles of highly crystalline individual nanotubes have been prepared through hydrothermal syntheses at 185 °C. The inhomogeneous broadening observed in their optical spectra is associated with the large distribution of crystal fields around Y3+(Ln3+) sites in the orthorhombic Pbcm Vernier-type Y6O5F8 host. Based on ratiometric analyses of the thermal evolution of intensities of near-infrared NIR (∼978 nm)-excited green upconversion emissions corresponding to 2H11/2, 4S3/2 → 4I15/2 Er3+ transitions, the temperature sensing behaviour of Er, Yb:Y6O5F8 was studied. This thermal sensor exhibits a very high sensitivity S = 0.0060 K−1 at physiological temperatures (22–50 °C), which surpasses the S value found for Er, Yb:β-NaYF4 at these temperatures, and a maximum S = 0.0082 K−1 at ∼225 °C. Also under NIR diode laser excitation, the color of the upconverted light from codoped Pr, Er, Yb:Y6O5F8 nanotubes can be selected by the control of the Pr3+ concentration and by the excitation regime and power density. Samples with low Pr3+ concentration emit green light, and the selection between bluish-green light and white light has been demonstrated with high Pr3+ concentration (2 mol%), under pulsed or continuous wave excitation, respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...