Dynamics of supercooled water in a biological model system of the amino acid l-lysine†
Abstract
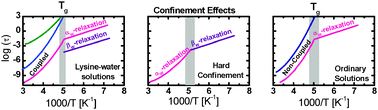
The dynamics of supercooled water in aqueous solutions of the single amino acid L-lysine has been studied by broadband dielectric spectroscopy. The chosen biological system is unique in the sense that the water content is high enough to fully dissolve the amino acid, but low enough to avoid crystallisation to ice at any temperature. This is not possible to achieve for proteins or other larger biomolecules, where either hydrated samples without ice or solutions with large quantities of ice, or a cryoprotectant sugar, have to be studied at low temperatures. Thus, it is a key finding to be able to study water and biomolecular dynamics in a non-crystallized and biologically realistic solution at supercooled temperatures. Here, we focus on the water dynamics in this unique biological solution of L-lysine and water. We show that this unique system also gives rise to unique water dynamics, since, for the first time, a continuation of a cooperative (α-like) water relaxation is observed after a crossover to a more local β-like water relaxation has occurred with decreasing temperature. This implies that the supercooled water in the biological solution shows a twofold relaxation behaviour, with one relaxation identical to the main relaxation of water in hard confinements and one relaxation almost identical to the main water relaxation in ordinary aqueous solutions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...