Unraveling the impact of hydroxylation on interactions of bile acid cationic lipids with model membranes by in-depth calorimetry studies†
Abstract
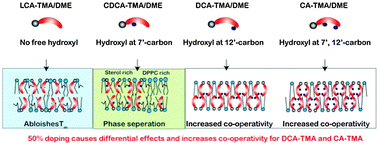
We used eight bile acid cationic lipids differing in the number of hydroxyl groups and performed in-depth differential scanning calorimetry studies on model membranes doped with different percentages of these cationic bile acids. These studies revealed that the number and positioning of free hydroxyl groups on bile acids modulate the phase transition and co-operativity of membranes. Lithocholic acid based cationic lipids having no free hydroxyl groups gel well with dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) membranes. Chenodeoxycholic acid lipids having one free hydroxyl group at the 7′-carbon position disrupt the membranes and lower their co-operativity. Deoxycholic acid and cholic acid based cationic lipids have free hydroxyl groups at the 12′-carbon position, and at 7′- and 12′-carbon positions respectively. Doping of these lipids at high concentrations increases the co-operativity of membranes suggesting that these lipids might induce self-assembly in DPPC membranes. These different modes of interactions between cationic lipids and model membranes would help in future for exploring their use in DNA/drug delivery.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...