Responses of polar organic compounds to different ionic environments in aqueous media are interrelated†
Abstract
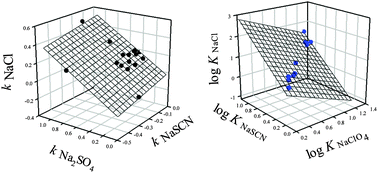
Solubilities of 17 polar organic compounds in aqueous solutions of Na2SO4, NaCl, NaClO4, and NaSCN at the salt concentrations of up to 1.0–2.0 M were determined and the Setschenow constant, ksalt, values were estimated. It was found that NaClO4 may display both salting-in and salting-out effects depending on the particular compound structure. The Setschenow constant values for all the polar compounds examined in different salt solutions are found to be interrelated. Similar relationships were observed for partition coefficients of nonionic organic compounds in aqueous polyethylene glycol–sodium sulfate two-phase systems in the presence of different salt additives reported previously [Ferreira et al., J. Chromatogr. A, 2011, 1218, 5031], and for the effects of different salts on optical rotation of amino acids reported by Rossi et al. [J. Phys. Chem. B, 2007, 111, 10510]. In order to explain the observed relationships it is suggested that all the effects observed originate as responses of the compounds to the presence of a given ionic environment and its interaction with the compounds by forming direct or solvent-separated ionic pairs. The response is compound-specific and its strength is determined by the compound structure and the type (and concentration) of ions inducing the response.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...