Vertically π-expanded coumarin – synthesis via the Scholl reaction and photophysical properties†
Abstract
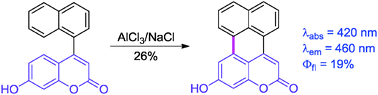
A short and efficient access to a unique type of π-expanded coumarin is achieved. The strategic placement of naphthalene at the 4-position of coumarin allowed us to fuse these two moieties via aromatic dehydrogenation under Scholl conditions. The intriguing optical properties of this π-expanded coumarin are discussed on the basis of quantum chemical calculations. The fluorescence quantum yield (∼20%) is significantly higher than that obtained for the classical 7-hydroxycoumarin. The ratio of emission versus radiationless deactivation is governed by the following factors: decrease in the oscillator strength of the SS transition (vs. perylene), low yield of intersystem crossing and strong internal conversion originating from the activity of the number of vibronic states.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...