Disintegration of graphene nanoribbons in large electrostatic fields
Abstract
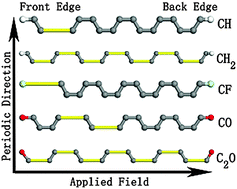
The deformation and disintegration of a graphene nanoribbon under external electrostatic fields are investigated by first principle quantum mechanical calculations to establish its stability range. Zigzag edges terminated by various functional groups are considered. By analyzing the phonon spectrum, the critical fracture field for each edge structure is obtained. It is found that different terminal groups on the zigzag graphene nanoribbons lead to different fracture patterns at different fracture fields. The failure mechanism is demonstrated to involve both the carbon bond alternation feature across the ribbon and the terminal group electronegativity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...