A Raman spectroscopic study of the carbon deposition mechanism on Ni/CGO electrodes during CO/CO2 electrolysis
Abstract
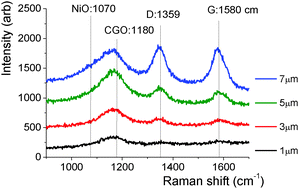
In situ and ex situ Raman analyses of porous Ni/CGO electrodes reveal differences in the amount, location and type of carbon formed during CO/CO2 electrolysis. The results demonstrate the limitations of optical in situ techniques applied to Solid Oxide Cells (SOCs) operated in electrolysis conditions. Increased carbon deposition close to the electrode–electrolyte interface is likely to be the result of high charge-transfer current in that area. The positive effect of a CGO interlayer on reducing carbon formation on the fuel electrode is demonstrated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...