Ex situ identification of the Cu+ long-range diffusion path of a Cu-based anode for lithium ion batteries†
Abstract
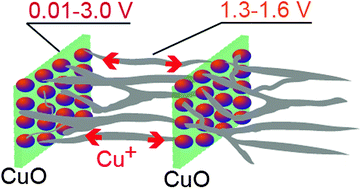
An ex situ observation was made by XRD patterns, SEM and TEM images, as well as cyclic voltammogram curves of CuO/Cu integrated anodes for lithium ion batteries. For the first time, the existence of a Cu+ ion long-range transfer path was identified at the potential widow of 1.30–1.60 V during both charging and discharging processes. Both SEM and TEM images show that these nanowires networks hanging CuO nanoparticles provide a Cu+ diffusion path within our designed CuO/Cu integrated anode. This work provides new insights into the conversion reaction of inorganic anode materials, and can favor the development of high-performance conversion anodes for lithium-ion batteries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...