Interaction of crystal water with the building block in Y2Mo3O12 and the effect of Ce3+ doping
Abstract
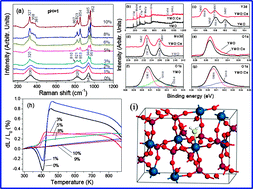
Ce3+ ions are introduced into the lattice of Y2Mo3O12 with a sol–gel method with the aim to reduce its hygroscopicity and pursue the interaction of crystal water molecules with the building block. It is found that Ce3+ ions occupy the positions of Y3+ in the lattice and have the function of expelling crystal water molecules in the microchannels so that the number of crystal water molecules decreases significantly as the Ce3+ content increases and a complete depletion of the crystal water is achieved when the content of Ce3+ is higher than 8 mol%. Based on the binding energy changes of Mo 3d and Y 3d with and without Ce3+ in the lattice, the configuration of the crystal water in the building block is deduced, namely, a crystal water serves as a spring with its O2− pointing to the Y3+ in an octahedron and with its H+ approaching the next nearest O2− in the Y–O–Mo bridge. With such a configuration, the effects of the crystal water on the thermal expansion properties of Y2Mo3O12 and the like are explained. It is also shown that the number of crystal water molecules per molecular formula can be quantified by the full width at half maximum of the Raman bands or relative intensity with linear relationships, suggesting that Raman spectroscopy can be a potential tool in quantifying crystal water molecules at room temperature in this or related materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...