Unusual electroluminescence from n-ZnO@i-MgO core–shell nanowire color-tunable light-emitting diode at reverse bias†
Abstract
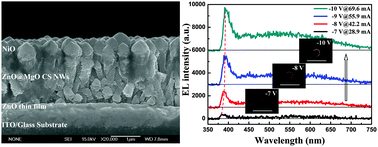
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) based on n-ZnO@i-MgO core–shell (CS) nanowires (NWs) are herein demonstrated and characterized. MgO insulating layers were rationally introduced as shells to modify/passivate the surface defects of ZnO NWs. A high-quality ZnO/MgO interface was attained and the optically pumped near-band-edge emission of the bare ZnO NWs was greatly enhanced after cladding i-MgO shells. Electroluminescence (EL) spectra measured in the whole UV-visible range revealed that light emission can only be detected when LEDs were applied with reverse bias. Moreover, the emission color can be tuned from orange to bright white with increasing reverse bias. We explored these interesting results tentatively in terms of the energy-band diagram of the heterojunction and it was found that the interfacial i-MgO shells not only acted as an insulator to prevent a short circuit between the two electrodes, but also offered a potential energy difference so that electron tunneling was energetically possible, both of which were essential to generate the reverse-bias EL. The dipole-forbidden d–d transitions by the Laporte selection rule in the p-NiO might be the reason to why there is no light being detected from the CS NW LED under forward bias. It is hoped that this simple and facile route may provide an effective approach in designing low-cost CS NW LEDs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...