QM/MM studies of the mechanism of unusual bifunctional fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase/phosphatase†
Abstract
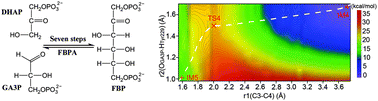
Archaeal fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase/phosphatase (FBPA/P) is a newly identified unusual bifunctional enzyme (Nature, 2010, 464, 1077), which contains one single catalytic domain but catalyzes two chemically distinct reactions of gluconeogenesis. It is different from the ordinary enzymes whose active sites are responsible for a specific reaction. To explore the catalytic characteristic of FBPA/P, the aldol condensation mechanism of bifunctional FBPA/P has been investigated using quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) method. The whole reaction process can be divided into two half-reactions involving seven elementary steps. A Schiff base intermediate is theoretically confirmed, agreeing well with the recently resolved crystal structures (Nature, 2011, 478, 538). The free energy barrier of the rate-limiting step is calculated to be 22.2 kcal mol−1, which is a concerted process of a nucleophilic attack by the enolic carbon to the ketonic carbon and a proton transfer from Tyr229 to the ketonic oxygen. Lys232 plays an important role in forming a Schiff base intermediate with the substrate (DHAP). Tyr229 functions as a proton shuttle during the catalysis. This is the first theoretical study on the aldol condensation mechanism of FBPA/P, which may provide useful information for understanding bifunctional enzymes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...