In situ IR spectroscopic studies of Ni surface segregation induced by CO adsorption on Cu–Ni/SiO2 bimetallic catalysts
Abstract
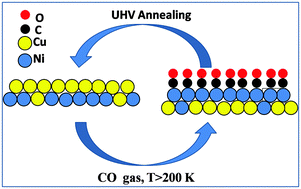
It is of great importance to study the catalytic structures under real reaction conditions especially for the bimetallic catalysts, where facile surface restructure or surface segregation can be driven by adsorbate adsorption. Here, we report CO interaction with Cu–Ni/SiO2 bimetallic model catalysts studied by CO temperature programmed desorption (TPD) and in situ CO polarization modulation infrared reflection absorption spectroscopy (PM-IRRAS) under CO pressures varying from ultrahigh vacuum (UHV) to near ambient pressure. Under UHV conditions, Cu is enriched on the surface of Cu–Ni/SiO2 bimetallic catalysts. CO spillover from Cu to Ni on Cu–Ni/SiO2 bimetallic catalysts has been observed at about 200 K under UHV conditions. In situ CO PM-IRRAS shows surface segregation of Ni on the Cu–Ni/SiO2 bimetallic catalysts induced by CO adsorption at ambient pressure CO. The behavior of CO induced surface segregation can lead to severe errors in Ni active site measurements by the selective CO chemisorption on Cu–Ni/SiO2 bimetallic catalysts.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...