Electromechanical properties of 1D ZnO nanostructures: nanopiezotronics building blocks, surface and size-scale effects†
Abstract
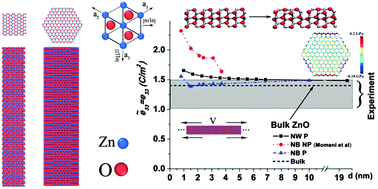
One-dimensional (1D) zinc oxide nanostructures are the main components of nanogenerators and central to the emerging field of nanopiezotronics. Understanding the underlying physics and quantifying the electromechanical properties of these structures, the topic of this research study, play a major role in designing next-generation nanoelectromechanical devices. Here, atomistic simulations are utilized to study surface and size-scale effects on the electromechanical response of 1D ZnO nanostructures. It is shown that the mechanical and piezoelectric properties of these structures are controlled by their size, cross-sectional geometry, and loading configuration. The study reveals enhancement of the piezoelectric and elastic modulus of ZnO nanowires (NW) with diameter d > 1 nm, followed by a sudden drop for d < 1 nm due to transformation of NWs to nanotubes (NTs). Degradation of mechanical and piezoelectric properties of ZnO nanobelts (NBs) followed by an enhancement in piezoelectric properties occurs when their lower dimension is reduced to <1 nm. The latter enhancement can be explained in the context of surface reconfiguration and formation of hexagon–tetragon (HT) pairs at the intersection of (2![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif)
![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) and (01
0) and (01![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) planes in NBs. Transition from a surface-reconstructed dominant to a surface-relaxed dominant region is demonstrated for lateral dimensions <1 nm. New phase-transformation (PT) kinetics from piezoelectric wurtzite to nonpiezoelectric body-centered tetragonal (WZ → BCT) and graphite-like phase (WZ → HX) structures occurs in ZnO NWs loaded up to large strains of ∼10%.
0) planes in NBs. Transition from a surface-reconstructed dominant to a surface-relaxed dominant region is demonstrated for lateral dimensions <1 nm. New phase-transformation (PT) kinetics from piezoelectric wurtzite to nonpiezoelectric body-centered tetragonal (WZ → BCT) and graphite-like phase (WZ → HX) structures occurs in ZnO NWs loaded up to large strains of ∼10%.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...