Complexation, dimerisation and solubilisation of methylene blue in the presence of biamphiphilic ionic liquids: a detailed spectroscopic and electrochemical study†
Abstract
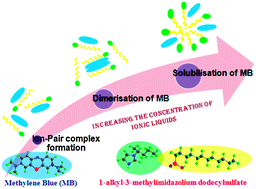
The interactions of methylene blue (MB), a redox active dye with surface active biamphiphilic ionic liquids (BAILs): 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium dodecylsulfate, [C4mim][C12OSO3] and 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium dodecylsulfate [C6mim][C12OSO3] have been investigated in aqueous medium to explore the candidature of surface active ionic liquids (ILs) in the field of dye–surfactant chemistry. Various thermodynamic, spectroscopic and electrochemical techniques such as conductivity, steady-state fluorescence, UV-visible absorption, and cyclic voltammetry (CV) have been used to obtain comprehensive information about MB–BAIL interactions. The presence of MB is seen to enhance the critical micellar concentration (cmc) of BAILs. The extent of interaction between the MB and BAILs varies with the concentration as well as the nature of BAILs. Different interactional phenomena such as the formation of ion-pair complexes, dimers, and solubilisation of monomers of MB have been observed in different concentration regimes of BAILs. A quantitative evaluation of the process of interaction between MB and BAILs has been made in terms of various micellar and binding parameters exploiting UV-visible absorption and CV measurements. Comparatively more hydrophobic [C6mim][C12OSO3] interacts strongly with MB as compared to [C4mim][C12OSO3] via hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...