Synthesis of CdWO4 nanorods and investigation of the photocatalytic activity†
Abstract
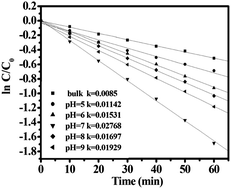
CdWO4 nanorod photocatalysts were synthesized by a hydrothermal method. CdWO4 nanorod photocatalysts showed highly efficient photocatalytic activity for the degradation of methylene blue under ultraviolet light irradiation. On the basis of the experiment results, the difference in photocatalytic activities of the samples was mainly attributed to surface area, surface hydroxyl groups and defects which can act as inactivation centers. Kinetic studies using radical scavenger technologies suggested that OH˙ radicals were the dominant photooxidants.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...