CsI:Tl+,Yb2+: ultra-high light yield scintillator with reduced afterglow†
Abstract
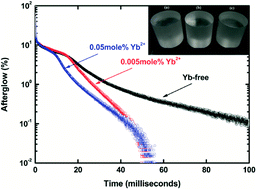
The afterglow problem has been preventing CsI:Tl single crystal scintillators from being used for applications in the field of computer tomography and high-speed imaging. We show that Yb2+ codoping in CsI:Tl can reduce it at least by one order of magnitude after 50 ms from X-ray cut-off compared to ordinary CsI:Tl. After optimization of the Yb2+ and Tl+ concentrations, the doubly doped CsI:Tl,Yb crystal exhibits an ultra-high light yield of 90 000 ± 6000 photons MeV−1, energy resolution 7.9%@511 keV and low afterglow level of about 0.035% at 80 ms. Simultaneous improvement in afterglow, light yield and energy resolution in CsI:Tl-based scintillators paves the way to its application in computer tomography and high-speed imaging. The physical mechanism and role of ytterbium ions in afterglow suppression are proposed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...