Enhancement of thermal stability in bismuth phosphate by Ln3+ doping for tailored luminescence properties†
Abstract
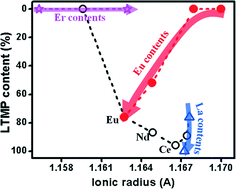
Bismuth phosphate represents one promising class of luminescent host materials, while its application is challenged by structural instability. In this work, a series of nanocrystals Bi1−xLnxPO4 (x = 0.02–0.09; Ln = La, Ce, Nd, Eu, Er) were prepared with an aim to find new routes in improving the structural stability of BiPO4 nanocrystals. Systematic sample characterization by XRD, SEM, TEM, and EDX indicates that doping a small amount of Ln3+ ions ≤9% could significantly stabilize the low temperature monoclinic phase (LTMP) by retarding the structure transition to the high temperature monoclinic phase (HTMP). For instance, after annealing at 900 °C, the relative contents of LTMP for co-doping of 5% La3+, 5% Nd3+, 5% Ce3+ with 2% Eu3+ were as high as 89%, 87%, and 96%, respectively, which are totally different from the un-doped BiPO4 at this temperature where LTMP is absent completely. This phenomenon has never been reported before for improving the stability of BiPO4, which has been explained in terms of lattice disorder due to the preference of the linking ways of rare earth–oxygen polyhedra and PO4 tetrahedra. With this abnormal structural stabilization, the luminescent properties of the Ln3+ doped LTMP, including emission intensity, lifetime, and quantum efficiency, were further tailored through simply tuning the calcination temperatures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...