A novel approach to understand the nucleation kinetics of α and γ polymorphs of glycine from aqueous solution in the presence of a selective additive through charge compensation mechanism
Abstract
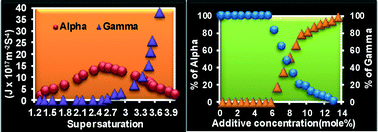
Nucleation of either the α or γ polymorph of glycine takes place by the dominant existence of dimer or monomer molecular conformations in solution. The effect of the selective additive sodium nitrate on the nucleation behaviour of the α and γ polymorphs of glycine is investigated both by experimental and analytical approaches. Experimentally, in situ nucleation tests were performed to measure the induction period of nucleation, type of nucleation and their proportionate appearance in the presence of different concentrations of the additive in solution. The internal structure of the nucleated crystallites was confirmed by single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. Nucleation of α and γ glycine takes place through a charge compensation mechanism. The incorporation of various concentrations of the additive changes the supersaturation of the system, which in turn changes the induction period of nucleation. Nucleation of the γ polymorph occurs at a critical concentration of the additive. Analytically, the nucleation parameters, such as interfacial energy, volume excess free energy, critical radius, critical energy barrier and nucleation rate of the α and γ polymorphs, were estimated based on classical nucleation theory from the experimentally measured induction periods. Variation in these theoretically deduced nucleation parameters with respect to the supersaturation in the system coincides well with the experimentally observed variation of these parameters during the kinetic processes observed within the experimental conditions. This correlation between the experimental and theoretical evidences provides a deeper insight in enabling us to have a clear idea as to what exactly happens inside the system. Moreover, the probability nucleation ratio of the α and γ polymorphs, estimated by powder X-ray diffraction and DSC followed by their structural confirmations, coincides very well with the experimentally observed values.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...