N-Methyl and peptoid scans of an autoinducing peptide reveal new structural features required for inhibition and activation of AgrC quorum sensing receptors in Staphylococcus aureus†
Abstract
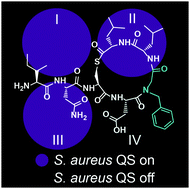
We report the first N-methyl and peptoid residue scans of a full-length autoinducing peptide (AIP), AIP-III, used by Staphylococcus aureus for quorum sensing (QS). Biological evaluation of these AIP-III analogues uncovered new features of the AIP-III scaffold that can be tuned to develop chemical probes of QS in all four groups of S. aureus (I–IV).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...