Excited state electron transfer after visible light absorption by the Co(i) state of vitamin B12†
Abstract
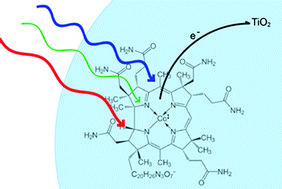
The first example of excited state electron transfer from cob(I)alamin is reported herein. Vitamin B12 was anchored to a mesoporous TiO2 thin film and electrochemically reduced to the cob(I)alamin form. Pulsed laser excitation resulted in rapid excited state electron transfer, ket > 108 s−1, followed by microsecond interfacial charge recombination to re-form cob(I)alamin. The supernucleophilic cob(I)alamin was found to be a potent photoreductant. The yield of excited state electron transfer was found to be excitation wavelength dependent. The implications of this dependence are discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...