Carbonic acid: molecule, crystal and aqueous solution
Abstract
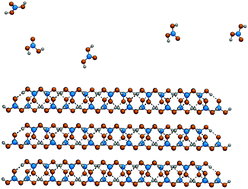
Carbonic acid (CA) is a crucial species in the equilibrium between carbon dioxide, water and many minerals. Yet many of its properties have either not been studied at all, or have been misunderstood. Its short lifetime in the presence of moisture has been a major stumbling block in efforts to studying it. Over the last two decades, there has been a sustained, albeit slow progress in the detection, synthesis and investigations of CA in its various phases – as a molecule in gas phase, in its crystalline state, as an adsorbate on mineral surfaces and in aqueous solutions. For instance, ultrafast time resolved spectroscopic experiments as well as molecular dynamics based free energy calculations using Kohn–Sham density functional theory have shown the pKa of CA to be around 3.5 which makes its acidity comparable to that of formic acid. The composition of its gas phase in terms of its conformer and oligomer population have also been examined. Thin films of crystalline carbonic acid polymorphs have been synthesized and characterized using infrared and Raman spectra. Given the difficulties associated in the conduct of experiments to investigate CA, computational modelling has played a significant role. Using a multi-tiered modelling approach, we have been able to examine several model crystal structures possessing distinctive hydrogen bonding motifs. Their vibrational spectra were compared against those obtained from experiments. A model crystal consisting of hydrogen bonded molecules in a chain-like fashion fits the experimental vibrational spectra of β-carbonic acid better than one in which the motif is two-dimensional (sheet-like). Under dry conditions, we predict such a crystal to be stable below 359 K at 1 atm. In this feature article, we provide a summary of our work on carbonic acid as well as review contributions from others.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...