The hydrophobic effect of nanoparticles composed of amphiphilic poly(γ-glutamic acid) on the degradability of the encapsulated proteins
Abstract
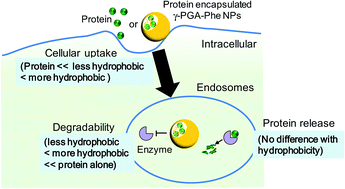
For the development of safe and effective next-generation vaccine carriers, their physicochemical properties (size, shape, surface charge, and hydrophobic/hydrophilic balance) are crucial to control their interactions (cellular uptake, intracellular degradability of the loaded antigen, and intracellular localization) with immune cells. Recently, the hydrophobicity of carriers affected the cellular uptake and immune response, which demonstrated that hydrophobicity is one of the most important factors to control the behaviors of the loaded antigens and carriers. In this study, we investigated the effect of the hydrophobicity of nanoparticles (NPs) composed of amphiphilic poly(γ-glutamic acid)-graft-phenylalanine ethyl ester (γ-PGA-Phe) with various grafting degrees of hydrophobic side chains on cellular uptake of the encapsulated antigens, their degradability, and their release behavior in the endosomal environment. These NPs could encapsulate proteins, and the degradability of the encapsulated proteins was changed by the hydrophobicity of NPs. On the other hand, the release behavior of the encapsulated proteins was not changed by the hydrophobicity of NPs. These results suggest that the intracellular behaviors of the encapsulated protein could be controlled by the hydrophobicity of NPs, and could result in the manipulation of the antigen-specific immune responses.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...