Influence of elastase on alanine-rich peptide hydrogels
Abstract
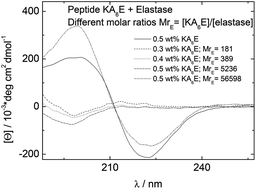
The self-assembly of the alanine-rich amphiphilic peptides Lys(Ala)6Lys (KA6K) and Lys(Ala)6Glu (KA6E) with homotelechelic or heterotelechelic charged termini respectively has been investigated in aqueous solution. These peptides contain hexa-alanine sequences designed to serve as substrates for the enzyme elastase. Electrostatic repulsion of the lysine termini in KA6K prevents self-assembly, whereas in contrast KA6E is observed, through electron microscopy, to form tape-like fibrils, which based on X-ray scattering contain layers of thickness equal to the molecular length. The alanine residues enable efficient packing of the side-chains in a beta-sheet structure, as revealed by circular dichroism, FTIR and X-ray diffraction experiments. In buffer, KA6E is able to form hydrogels at sufficiently high concentration. These were used as substrates for elastase, and enzyme-induced de-gelation was observed due to the disruption of the beta-sheet fibrillar network. We propose that hydrogels of the simple designed amphiphilic peptide KA6E may serve as model substrates for elastase and this could ultimately lead to applications in biomedicine and regenerative medicine.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...