Mesoporous nanogold–MnO2–poly(o-phenylenediamine) hollow microspheres as nanotags and peroxidase mimics for sensing biomolecules
Abstract
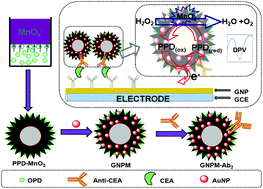
A new electrochemical immunosensor was designed for the determination of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) with sensitivity enhanced by using nanogold–poly(o-phenylenediamine)–manganese dioxide organic–inorganic hybrid nanostructures (GNPM) as nanotags and peroxidase mimics. Initially, mesoporous poly(o-phenylenediamine)–manganese dioxide (PPD–MnO2) hollow microspheres were synthesized by an inorganic/organic interfacial polymerization technique. Then gold nanoparticles were assembled onto the surface of PPD–MnO2, which were used for the labelling of the anti-CEA detection antibody (pAb2). The prepared GNPM nanotags were characterized using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), UV-vis absorption spectroscopy, N2 adsorption–desorption isotherm measurements and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The assay was carried out with a sandwich-type immunoassay format in pH 5.5 acetic acid-buffered saline solution containing 2.5 mmol L−1 H2O2. Experimental results indicated that the electrochemical immunosensor exhibited a wide dynamic range from 0.01 to 80 ng mL−1 towards the target CEA with a detection limit (LOD) of 6.0 pg mL−1. The immunosensor also displayed a good stability and acceptable reproducibility and selectivity. In addition, the methodology was evaluated by assaying 10 clinical serum samples, providing a good relationship between the electrochemical immunosensor and the commercialized electrochemiluminescent (ECL) method for determination of CEA.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...