Reliable on-site characterization of aromatic compounds adsorbed on porous particles with SERS in a dynamic adsorption-hydrocyclone separation process†
Abstract
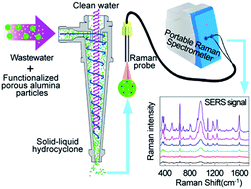
A novel method for reliable on-site characterization of aromatic compounds adsorbed on porous particles with surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) in a dynamic adsorption-hydrocyclone separation process (DAHS) was introduced. Aromatic compounds found in printing and dyeing wastewater were adsorbed on functionalized porous alumina particles (FPAPs). The SERS-active FPAPs were prepared by decorating and growing silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs, ∼70 nm diameter) on the surface of porous alumina particles (PAPs). Samples were then characterized with a portable Raman spectrometer. SERS offers quantitative analyses of the pollutants adsorbed on the surface of FPAPs directly and the quantity of benzidine adsorbed on porous particles was 20.5 mg kg−1. It shows that the SERS-DAHS technique could be readily applied to the quantitative characterization of aromatic compounds adsorbed on SERS-active FPAPs. Furthermore, both qualitative and quantitative detection of aromatic compounds in wastewater produced on-site were readily accomplished using the SERS-DAHS method and its analytical ability compares well with GC-MS and the detection results deviating between these two techniques was less than 10%. The results demonstrate that the SERS-DAHS method is straightforward, rapid, and preferable for the real-time detection and quantitative characterization of aromatic compounds/pollutants adsorbed on porous materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...