Fabrication of a novel Ti–TiO2–ZrO2 fiber for solid-phase microextraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography for sensitive determination of UV filters in environmental water samples†
Abstract
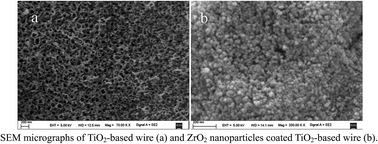
A novel Ti–TiO2–ZrO2 fiber for solid-phase microextraction (SPME) was fabricated by chemical oxidization of a Ti wire substrate and subsequent electrodeposition of ZrO2 nanoparticle coating. The chemically oxidized procedure afforded in situ fabrication of porous TiO2 nanostructures on a Ti wire and provided a desirable substrate for further deposition of ZrO2 nanoparticle coating. The best extraction capability was obtained by ZrO2 nanoparticles with a size distribution of 20–30 nm and a coating thickness of about 4.5 μm after 10 cyclic voltammetry scans. The main parameters affecting the Ti–TiO2–ZrO2 fiber for SPME of ultraviolet (UV) filters were investigated coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography with UV detection. A good linearity was achieved in the range of 0.5–500 μg L−1 with correlation coefficients higher than 0.996. Limits of detection were 0.032–0.082 μg L−1 (S/N = 3). The single fiber repeatability ranged from 4.3% to 12% and the fiber-to-fiber reproducibility ranged from 4.3% to 11% for SPME of spiked water with 50 μg L−1 UV filters (n = 5). Furthermore this fiber has high stability, long service time and high extraction capability for UV filters compared to the commercially available polymeric fibers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...