Determination and quantitative analysis of designer drugs in human urine by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
Abstract
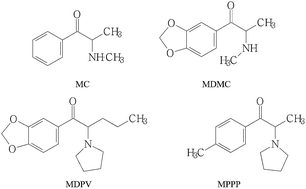
A robust liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-ion trap mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-ITMS) method was developed and utilized for the determination and quantitative analysis of four designer drugs in human urine. Designer drugs, including methcathinone (MC), 3,4-methylenedioxymethcathinone (MDMC), methylenedioxy-pyrovalerone (MDPV) and 4′-methyl-α-pyrrolidinopropiophenone (MPPP) were determined by LC-ESI-ITMS under the optimal chromatographic separation conditions, and the precursor and major product ions of them were monitored in positive ion detection mode as m/z 164.0/146.0, m/z 208.0/190.1, m/z 276.2/205.0 and m/z 218.1/147.0, respectively. Linear calibration curves showed good linearity in the range 0.010–5.00 μg mL−1, with coefficients of greater than 0.9988. The method was validated with the intra-day and inter-day precisions represented by relative standard deviation of less than 5.3% in human urine, and the recoveries from spiked urine samples varied from 79.5% to 94.6%. The obtained results indicated that the method was rapid, sensitive and selective, and it could be applied in the determination of designer drugs in addict cases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...