Development of a sensitive and specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the determination of fludioxonil residues in fruit juices
Abstract
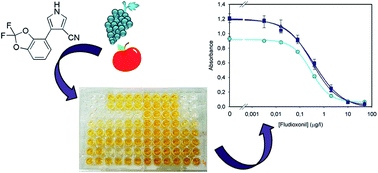
Fludioxonil is a fungicide with a singular mode of action that is widely employed in the treatment of fruit crops. A competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (cELISA) has been developed and validated for the determination of residues of this fungicide in fruit juices. A collection of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against the fungicide fludioxonil has been produced and characterized using direct and indirect cELISAs. The high affinity achieved (IC50 lower than 0.5 μg L−1) considerably improved that obtained with previous polyclonal antibodies. The proposed cELISA was applied to the analysis of fludioxonil residues in apple juice and red grape must samples with a limit of quantification of 5 and 10 μg L−1, respectively. A validation of the method has been performed in terms of sensitivity, selectivity, trueness, precision, and robustness. Finally, blind-spiked samples were measured by the proposed cELISA and by a gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) method, with equivalent results by both methodologies.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...