Pressurized liquid extraction as an alternative to the Soxhlet extraction procedure stated in the US EPA method TO-13A for the recovery of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons adsorbed on polyurethane foam plugs
Abstract
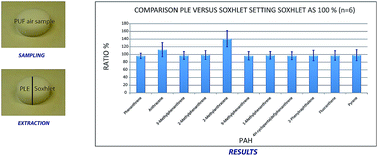
The aim of the present study was to develop a pressurized liquid extraction (PLE) method as an alternative to the relatively time consuming Soxhlet extraction procedure described in the United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) method TO-13A for the extraction of PAHs adsorbed onto polyurethane foam plugs (PUFs). For this purpose PUF air samples were collected and split into two parts: one part extracted using PLE and the other one using Soxhlet extraction. Comparable PAH concentrations were obtained upon analysis of the extracts showing that the PLE method developed in this work is a more convenient choice than the commonly used Soxhlet extraction technique proposed by US EPA for the determination of PAHs in air samples. In fact, the developed PLE method required shorter assay times (minutes versus hours), less solvent consumption and simpler operational methods. The exhaustiveness of the developed PLE method was evaluated using repeat static extraction cycles, demonstrating an extraction efficiency for the PAHs of greater than 99%. The PLE method was then applied to diesel exhaust and wood smoke PUF samples showing an extraction efficiency for the PAHs of greater than 93% and 96%, respectively. Furthermore, a PLE method for PUF cleaning was developed as well and employed as an alternative to Soxhlet extraction. The PLE methods developed for cleaning and extracting PUFs presented in this work are suitable to be used in mutagenicity studies using the Ames Salmonella assay as no mutagenicity was found in the PLE generated blanks.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...