LC-ESI-MS/MS studies on saxagliptin and its forced degradation products†
Abstract
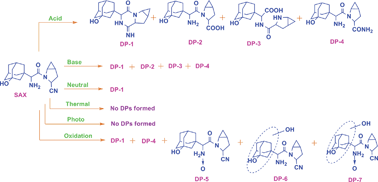
The objective of this study was to explore the degradation behaviour of saxagliptin (SAX), a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor, under hydrolytic (acidic, alkaline, and neutral), oxidative, photolytic, and thermal stress conditions as per prescribed International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) guidelines. The drug was found to be labile under hydrolytic and oxidative stress conditions, whereas it was stable under photolytic and thermolytic stress conditions. A total of seven degradation products (DPs) were identified, and their chromatographic separation was accomplished on a C18 column (100 × 4.6 mm; 5 μm) using a mobile phase consisting of 10 mM ammonium formate and methanol in a gradient elution mode. All of the stressed samples were subjected to LC-MS, LC-MS/MS, and ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS analysis. SAX and its DPs were characterized based on elemental composition and isotopic distribution information from full scan mode and fragmentation patterns obtained from MS/MS and HRMS experiments. Structural elucidation of DPs was achieved by comparing their fragmentation patterns with that of SAX. The developed LC method was validated as per ICH guidelines with respect to specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, and robustness.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...