Chemical analysis of the Tibetan herbal medicine Carduus acanthoides by UPLC/DAD/qTOF-MS and simultaneous determination of nine major compounds
Abstract
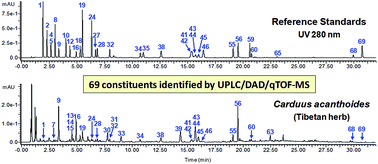
Carduus acanthoides is a traditional Tibetan herbal medicine for the treatment of hematemesis, hematuria, and menorrhagia. Despite its multiple biological activities, comprehensive chemical analysis of this herb has not been reported, so far. In this study, chemical constituents of C. acanthoides were analyzed by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode array detection and time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC/DAD/qTOF-MS). The methanol extract of C. acanthoides was separated on an ACQUITY HSS T3 column (1.8 μm, 150 mm × 2.1 mm) and eluted with acetonitrile–water (containing 0.1% formic acid). Constituents were identified by UV and HRMS in the negative ion mode. A total of 69 compounds were identified from C. acanthoides, including 35 flavonoids, 17 quinic acids, 7 phenolic acid glycosides, 5 phenylethanoid glycosides, 3 coumarins, and 2 phenolic acids. Among them, 31 compounds were unambiguously characterized by comparing with reference standards. Furthermore, a UPLC/UV (340 nm) method was established to simultaneously determine 3 quinic acids and 6 flavonoids, including neochlorogenic acid (9), chlorogenic acid (16), cryptochlorogenic acid (18), kaempferol 3-O-rhamnoside-7-O-glucoside (32), luteolin 7-O-glucosyl-(1→2)-glucoside (34), luteolin 7-O-glucoside (38), luteolin 7-O-6′′′-O-acetyl-glucosyl-(1→2)-glucoside (44), kaempferol 3-O-rhamnoside (55), and chrysoeriol 7-O-6′′′-O-acetyl-glucosyl-(1→2)-glucoside (56). All analytes showed good linearity (r2 ≥ 0.998) with an LOD of 0.077–0.120 μg mL−1. These nine compounds accounted for 2.1–3.5‰ of the herb.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...