Amplified electrochemiluminescence of lucigenin triggered by electrochemically reduced graphene oxide and its sensitive detection of bisphenol A
Abstract
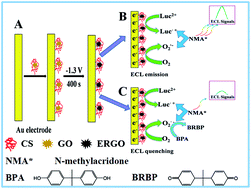
An amplified and stable electrochemiluminescent signal of lucigenin was observed on an electrochemically reduced graphene oxide-containing sensing platform. Herein, chitosan was used as an excellent dispersant, which favors the better dispersion of graphene oxide in solution and improved electrochemical reduction of graphene oxide. The electrochemically reduced graphene oxide showed outstanding conductivity which was propitious to the transfer of electrons, leading to the enhancement of the electrochemiluminescent signals of lucigenin. In addition, bisphenol A, as a classical food borne pollutant, was first detected due to its strong inhibiting action of the electrochemiluminescent response of lucigenin. Then, we studied the quenched electrochemiluminescent system and the possible mechanism of the platform in detail. Under optimum conditions, the proposed electrochemiluminescent sensor exhibited a linear response range from 1.0 × 10−9 mol L−1 to 1.0 × 10−4 mol L−1 with a low detection limit of 3.0 × 10−10 mol L−1 for bisphenol A, which might find promising applications in developing a new type of biosensor.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...