Identification of in vivo components in rats after oral administration of lotus leaf flavonoids using ultra fast liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry
Abstract
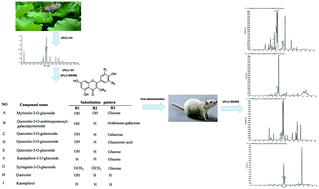
The herb of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) leaves is the traditional Chinese medicine He Ye, which is commonly used to treat sunstroke, assuage thirst, and cure both diarrhea and fever in China. Lotus leaves are rich in flavonoids, which exhibit various biological activities. However, the in vivo components, including parent compounds and their metabolites after consumption of the leaves have not been investigated extensively. In the present study, a method based on ultra fast liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (UFLC-MS/MS) was established to identify the in vivo components in rats after oral administration of a lotus leaf flavonoid extract. Plasma and urine samples were collected before and after dosing and treated by liquid–liquid extraction with ethyl acetate, and followed by UFLC-MS/MS assay. Q1 (first quadrupole) full scan combined with multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) survey scan were used for the detection of parent flavonoids and their metabolites. MRM-information dependent acquisition (IDA) of enhanced product ions (MRM-IDA-EPI) was used for the structural identification of detected components. A total of thirty-seven components were identified, including quercetin-3-O-glucuronide, quercetin-3-O-glucoside, quercetin-3-O-galacoside, quercetin and kaempferol, as well as their methylation, glucuronidation, and sulfonation metabolites. The result may help better understand the pharmacological activities of the traditional Chinese medicine He Ye.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...