Analysis of trace bromadiolone and brodifacoum in environmental water samples by ionic liquid ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and LC-MS/MS
Abstract
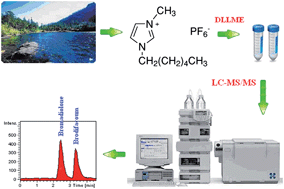
An ionic liquid-based ultrasonic-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (IL-USA-DLLME) method was proposed for highly effective extraction of trace bromadiolone and brodifacoum in environmental water samples. The ionic liquid, 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate [C6mim][PF6] was quickly disrupted by ultrasonication and dispersed in water as fine droplets. At this stage, the analytes were extracted into the fine ionic liquid droplets. After centrifugation, the concentration of the enriched rodenticides in the sedimented phase was determined. Extraction conditions including extraction solvent, dispersive solvent volume, pH, ultrasonic time and centrifugation time were investigated thoroughly. Compared with the conventional solvent extraction, the proposed approach exhibited higher efficiency, which indicated the IL-USA-DLLME method was an efficient, rapid and simple sample preparation technique. Under optimized extraction conditions, the enrichment factors were up to 122–137 times, achieving the limits of quantitation, which based on the signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) of 10 were 0.005 μg L−1 for both. The linearities for both analytes were in the range of 0.005–1.0 μg L−1 with a correlation coefficient >0.999, and the recoveries were between 88.8–98.3% with relative standard deviations (RSDs) between 1.1% and 9.3%. The proposed method shows high reproducibility, and it is suitable for analysis of trace bromadiolone and brodifacoum in environmental water samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...