Magnetic separation–enrichment-mediated signal amplification for a simple and sensitive fluorometric assay of biotin
Abstract
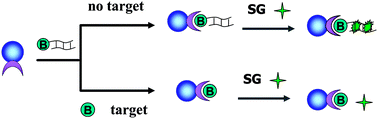
Many types of separation-based sensing systems have been reported for biotin assays. Although these conventional strategies provide an accurate and sensitive detection of biotin, there are still some inconveniences that exist, such as the complex sample treatment, time-consuming assay process, and technical expertise as well as the sophisticated equipment. We have addressed these limitations and report herein the proof-of-principle of a dual strategy which combines magnetic separation–enrichment with DNA–SG (SYBR Green I)-based signal amplification to develop a simple and sensitive fluorometric biotin sensing strategy. This method is based on the competition scheme where biotin and the biotinylated dsDNA compete for the binding sites of streptavidin coated on magnetic bead (SA-MB) surfaces. After separation and enrichment under the magnetic field, the fluorescence emission intensity or fluorescent images can be obtained by addition of SG, which is inversely related to biotin concentrations. Using the biotin solution as a model system, we demonstrated that our assay can detect biotin at a concentration as low as 1.19 ng mL−1 in one hour which highly excels traditional assays such as HPLC. Moreover, we also used the proposed method to measure the biotin level in actual samples, for example flour and peanuts, for which satisfactory results were obtained.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...